Electric Ships Market Key Companies and SWOT Analysis by 2028
Electric Ships Market Forecast to 2028 - Analysis By Type (Battery Electric Ships, Plug-In Hybrid Electric Ships, and Hybrid Electric Ships), Power (Less Than 75 KW, 75 - 150 KW, 151 - 745 KW, 746 - 7560 KW, and More Than 7560 KW), Range (Less Than 50 Km, 50 - 100 Km, 101 - 1000 Km, and More Than 1000 Km), and Ship Type (Cruise Ships, Ferries, Tankers, Bulk Carriers, Fishing Vessels, Destroyers, Aircraft Carriers, and Others)
Historic Data: 2019-2020 | Base Year: 2021 | Forecast Period: 2022-2028- Report Date : Mar 2022
- Report Code : TIPRE00007455
- Category : Automotive and Transportation
- Status : Published
- Available Report Formats :


- No. of Pages : 164
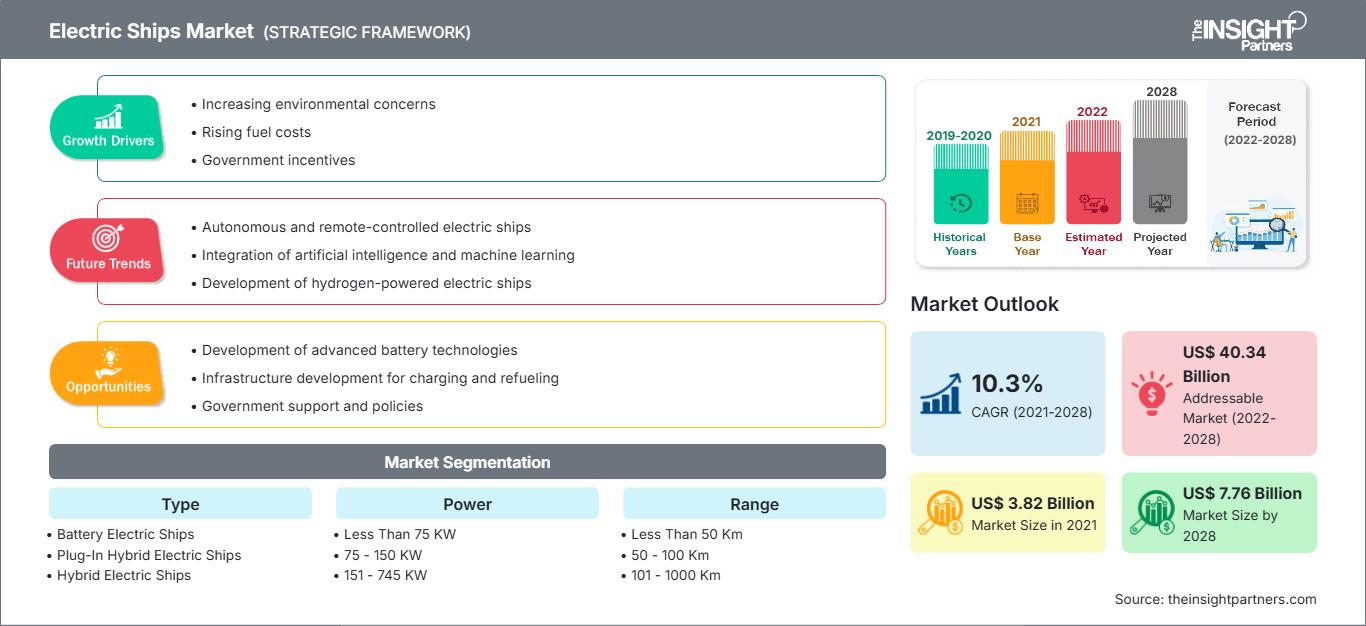
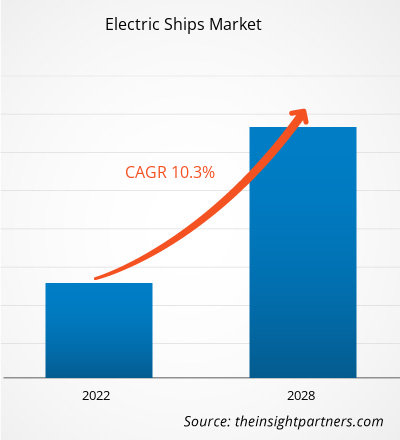
The electric ships market was valued US$ 3.82 billion in 2021, it is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 10.3% from 2021 to 2028.
An electric boat is any boat or ship whose primary propulsion technology is an electric drive system. It can be a full-battery electric, hydrogen fuel cell electric, electric hybrid boat or ship, from tugboats, ferries, cargo ships, and barges to tour boats, fishing trawlers, cruising yachts, and unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs). Electric ships are driven electrically, unlike conventional diesel engine ships. These ships use a battery storage device as their power source to drive electric motors. Numerous types of batteries can be used in an electric ship, including lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries, and fuel cells. Electric ships are mainly ferries and small passenger ships on inland waterways that sail entirely with electricity. They travel only short distances with ~80 km in a single charge. Further, solar-powered ships are also used in lightweight ships that require low power output. However, the power requirements of cargo ships cannot be fulfilled by a fully electric system due to heavyweight; hence cargo ships are utilizing a hybrid diesel-electric system.
Customize This Report To Suit Your Requirement
Get FREE CUSTOMIZATIONElectric Ships Market: Strategic Insights
-
Get Top Key Market Trends of this report.This FREE sample will include data analysis, ranging from market trends to estimates and forecasts.
Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on Electric Ships Market
The COVID-19 pandemic adversely affected the electric ships market. The pandemic led to unparalleled global impacts on human mobility. In the ocean, ship-based activities are affected due to severe restrictions on human movements and changes in consumption of goods. A few countries have closed their cruise industry due to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, some cruise lines are trying to resume their activities during the pandemic. Human activities in the ocean have been radically changed by the COVID-19 pandemic, with reports of port restrictions and shifts in consumption patterns impacting multiple maritime sectors, fisheries, passenger ferries, and cruise ships. However, in some regions, the shipping of goods was declared essential during the lockdown, which created a lucrative opportunity for the electric ships market.
Electric Ships Market Insights
Rise in Adoption of Hybrid and Electric Propulsion Systems for Retrofitting Ships
Retrofitting ships is gaining interest and attracting shipowners/shipbuilders to extend the lifetime of their existing ships. Such a process provides a chance to reduce fuel consumption and stay updated with the latest eco-friendly solutions as a cost-effective procedure. Retrofitting is becoming a common practice in the maritime industry. Shipbuilders are moving toward automation, integrating newly built ships, and retrofitting existing ships with hybrid and electric propulsion systems. This system is a convenient choice for retrofitting outdated ships with enormous retrofit potential, including ferries, container vessels, cruise ships, tugboats, and general cargo ships. Shipbuilders choose to retrofit ships with a hybrid-electric propulsion system or a fully electric propulsion system as it is a relatively cheaper option than purchasing a new ship. Further, several European shipbuilders are actively retrofitting their current ship fleet with hybrid and electric propulsion systems. For instance, according to the article published by the Riviera Maritime Media Ltd, in March 2020, the offshore supply vessel (OSV) owners invested in retrofitting diesel-electric/LNG-powered fleets with battery-hybrid propulsion in a move that is paying off for the charterer, owner, and the environmental issues in Norway. These factors have resulted in the adoption of hybrid and electric propulsion systems for retrofitting ships.
Type-Based Market Insights
Based on type, the electric ships market is segmented into battery electric ships, plug-in hybrid electric ships, and hybrid electric ships. The hybrid electric ships segment led the market in 2020. The reliability offered by hybrid electric ships supports its demand owing to the use of supplementary propulsion systems and higher speed, which can reduce the risk of failure and cover greater distances in less time. Besides, hybrid electric vessel propulsion can be propelled in two ways—electrical (via diesel-electric or battery power-driven) or mechanical (direct diesel drove). Furthermore, ship owners or shipping and logistic companies across the globe prefer hybrid electric ships as they enable lower fuel consumption and help reduce operational costs. The use of diesel-electric propulsion at low power and direct diesel-driven propulsion in need of high power that is inland water sailing with different speed conditions enables a reduction in operational cost in the electric ship. This is a smarter way to use available energy and save on fuel costs by using hybrid electric ship propulsion.
Players operating in the electric ships market adopt strategies, such as mergers, acquisitions, and market initiatives, to maintain their positions in the market. A few developments by key players are listed below.
- In November 2021, BAE Systems launched a next-generation power and propulsion system to help marine operators reach zero emissions. It provides a flexible solution improving electrical efficiency and vessel range, increasing propulsion power, and simplifying installation.
- In September 2020, Kolumbus (a mobility company) and Fjellstrand (shipbuilder) signed a contract to deliver the world’s first fully electrical fast ferry. This project had received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program.
Based on type, the electric ships market is segmented into battery electric ships, plug-in hybrid electric ships, and hybrid electric ships. Based on the power, the electric ships market is segmented into less than 75 kW, 75-150 kW, 151-745 kW, 746-7560 kW, and more than 7560 kW. Based on range, the electric ships market is categorized into less than 50 km, 50-100 km, 101-1000 km, and more than 1000 km. Based on ships type, the electric ships market is segmented into cruise ship, ferries, tankers, bulk carriers, fishing vessels, destroyers, aircraft carriers, and others. By geography, the electric ships market is segmented into five major regions—North America, Europe, Asia Pacific (APAC), Middle East & Africa (MEA), and South America (SAM).
Electric Ships Market Regional InsightsThe regional trends and factors influencing the Electric Ships Market throughout the forecast period have been thoroughly explained by the analysts at The Insight Partners. This section also discusses Electric Ships Market segments and geography across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East and Africa, and South and Central America.
Electric Ships Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market size in 2021 | US$ 3.82 Billion |
| Market Size by 2028 | US$ 7.76 Billion |
| Global CAGR (2021 - 2028) | 10.3% |
| Historical Data | 2019-2020 |
| Forecast period | 2022-2028 |
| Segments Covered |
By Type
|
| Regions and Countries Covered |
North America
|
| Market leaders and key company profiles |
|
Electric Ships Market Players Density: Understanding Its Impact on Business Dynamics
The Electric Ships Market is growing rapidly, driven by increasing end-user demand due to factors such as evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and greater awareness of the product's benefits. As demand rises, businesses are expanding their offerings, innovating to meet consumer needs, and capitalizing on emerging trends, which further fuels market growth.
- Get the Electric Ships Market top key players overview
Company Profiles
- BAE Systems
- Duffy Electric Boat Company
- Fjellstrand AS
- X Shore
- General Dynamic Electric Boat
- Hurtigruten
- MAN Energy Solutions
- PortLiner
- Siemens Energy
- VARD AS
Frequently Asked Questions
Naveen is an experienced market research and consulting professional with over 9 years of expertise across custom, syndicated, and consulting projects. Currently serving as Associate Vice President, he has successfully managed stakeholders across the project value chain and has authored over 100 research reports and 30+ consulting assignments. His work spans across industrial and government projects, contributing significantly to client success and data-driven decision-making.
Naveen holds an Engineering degree in Electronics & Communication from VTU, Karnataka, and an MBA in Marketing & Operations from Manipal University. He has been an active IEEE member for 9 years, participating in conferences, technical symposiums, and volunteering at both section and regional levels. Prior to his current role, he worked as an Associate Strategic Consultant at IndustryARC and as an Industrial Server Consultant at Hewlett Packard (HP Global).
- Historical Analysis (2 Years), Base Year, Forecast (7 Years) with CAGR
- PEST and SWOT Analysis
- Market Size Value / Volume - Global, Regional, Country
- Industry and Competitive Landscape
- Excel Dataset
Recent Reports
Testimonials
The Insight Partners' SCADA System Market report is comprehensive, with valuable insights on current trends and future forecasts. The team was highly professional, responsive, and supportive throughout. We are very satisfied and highly recommend their services.
RAN KEDEM Partner, Reali Technologies LTDsI requested a report on a very specific software market and the team produced the report in a few days. The information was very relevant and well presented. I then requested some changes and additions to the report. The team was again very responsive and I got the final report in less than a week.
JEAN-HERVE JENN Chairman, Future AnalyticaWe worked with The Insight Partners for an important market study and forecast. They gave us clear insights into opportunities and risks, which helped shape our plans. Their research was easy to use and based on solid data. It helped us make smart, confident decisions. We highly recommend them.
PIYUSH NAGPAL Sr. Vice President, High Beam GlobalThe Insight Partners delivered insightful, well-structured market research with strong domain expertise. Their team was professional and responsive throughout. The user-friendly website made accessing industry reports seamless. We highly recommend them for reliable, high-quality research services
YUKIHIKO ADACHI CEO, Deep Blue, LLC.This is the first time I have purchased a market report from The Insight Partners.While I was unsure at first, I visited their web site and felt more comfortable to take the risk and purchase a market report.I am completely satisfied with the quality of the report and customer service. I had several questions and comments with the initial report, but after a couple of dialogs over email with their analyst I believe I have a report that I can use as input to our strategic planning process.Thank you so much for taking the extra time and making this a positive experience.I will definitely recommend your service to others and you will be my first call when we need further market data.
JOHN SUZUKI President and Chief Executive Officer, Board Director, BK TechnologiesI wish to appreciate your support and the professionalism you displayed in the course of attending to my request for information regarding to infectious disease IVD market in Nigeria. I appreciate your patience, your guidance, and the fact that you were willing to offer a discount, which eventually made it possible for us to close a deal. I look forward to engaging The Insight Partners in the future, all thanks to the impression you have created in me as a result of this first encounter.
DR CHIJIOKE ONYIA MANAGING DIRECTOR, PineCrest Healthcare Ltd.Reason to Buy
- Informed Decision-Making
- Understanding Market Dynamics
- Competitive Analysis
- Identifying Emerging Markets
- Customer Insights
- Market Forecasts
- Risk Mitigation
- Boosting Operational Efficiency
- Strategic Planning
- Investment Justification
- Tracking Industry Innovations
- Aligning with Regulatory Trends



















 Get Free Sample For
Get Free Sample For