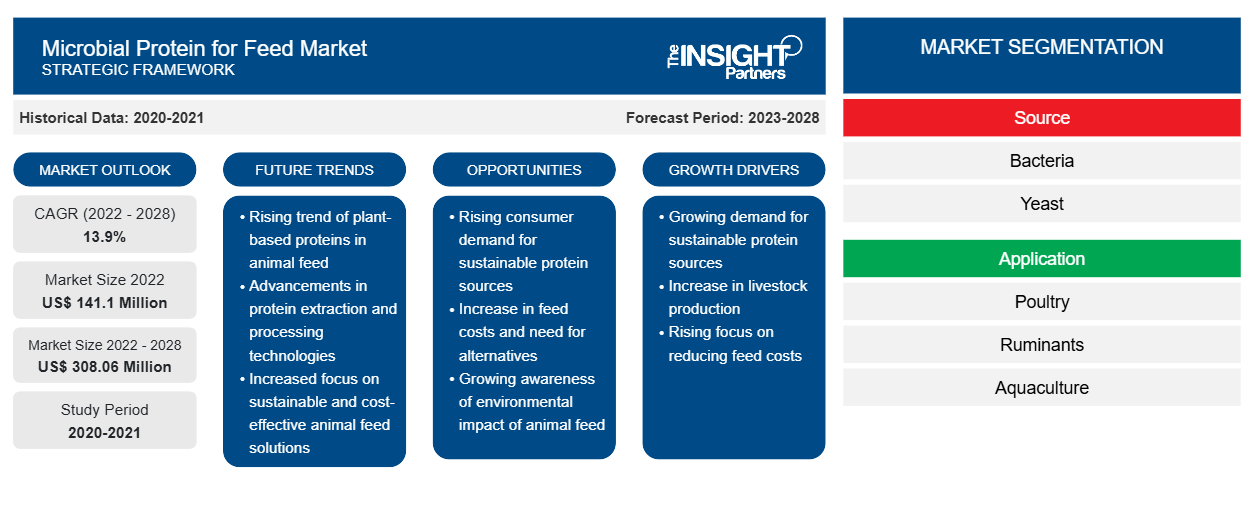
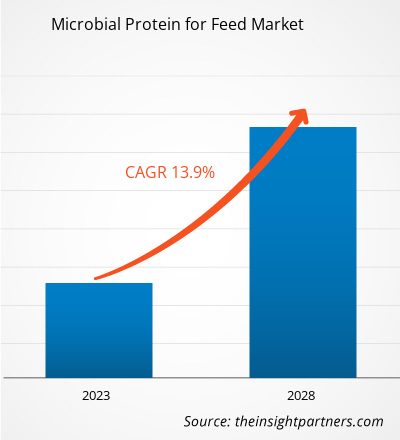
The microbial protein for feed market size is expected to grow from US$ 141,095.88 thousand in 2022 to US$ 308,055.17 thousand by 2028; it is estimated to register a CAGR of 13.9% from 2022 to 2028.
Microbial protein is one of the significant sources of crude protein. There are many nutritional benefits of including microbial protein in animal feed. Microbial protein contains more than 70% crude protein, whereas soymeal contains 40–50% crude protein, and fish meal contains 60–65% crude protein. Moreover, it has an ideal amino acid profile, including higher valine, tryptophan, isoleucine, and leucine compared to fish meals. Microbial protein is one of the excellent alternatives to conventional sources of proteins such as soybean and fish meal. It is produced using cost-effective substrates such as industrial gases (carbon dioxide, methane, and natural gas), wastewater, and poultry waste (feathers) fermented in a reactor using bacteria, yeast, fungi, or microalgae. Thus, various nutritional benefits of adding microbial protein to livestock diets and rising sustainability concerns are driving the microbial protein for feed market growth.
In 2021, Europe held the largest share of the global microbial protein for feed market. According to the European Feed Manufacturers’ Federation (FEFAC), pig feed production increased by 2.9% in 2020, despite the continued spread of African Swine Fever (ASF) in the region and its impact on pig farming. Several European countries increased their exports to China, benefiting from Germany’s export ban, which led to a surge in pig feed production in 2020. With the rising levels of animal feed production, manufacturers are looking for sustainable feed additives, as animal-sourced and plant-sourced feed additives are not perceived as environment-friendly nowadays. Imported feed materials, such as soy, threaten natural resources and biodiversity. Thus, the demand for microbial protein is increasing among animal feed manufacturers.
Customize This Report To Suit Your Requirement
Get FREE CUSTOMIZATIONMicrobial Protein for Feed Market: Strategic Insights
-
Get Top Key Market Trends of this report.This FREE sample will include data analysis, ranging from market trends to estimates and forecasts.
Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on microbial protein for feed market
The feed industry faced crucial challenges such as a shortage of raw materials and laborers, a surge in raw material prices, and disruptions in distribution networks due to lockdowns, travel bans, trade limitations, manufacturing unit shutdowns, and other government-levied restrictions across the globe. This hampered the manufacturing activities of various companies in the animal feed industry, subsequently resulting in increased prices of feed ingredients. In European Union, about two-thirds of member states pointed out the spike in feed prices in the livestock industry during the pandemic. Moreover, during the peak of the pandemic, China closed livestock and poultry trading and slaughter markets in most of the regions. Such barriers in the livestock industry hampered the demand for feed ingredients which had a negative impact on the demand for microbial protein for feed during the pandemic.
In 2021, various economies resumed operations as their governments announced relaxations in the previously imposed restrictions, which boosted the global marketplace. Further, manufacturers were permitted to operate at full capacities, which helped them overcome the demand and supply gap and other repercussions.
Market Insights
Government and Private Sector Investments to Have Positive Impact on Microbial Protein for Feed Market Growth
Climate change and overexploitation of natural resources such as land and water are the leading sustainability concerns in livestock and animal feed industries. As a result, governments of various countries across the globe are funding companies that manufacture animal feed and ingredients using sustainable practices to reduce their overall carbon footprint and support the circular economy growth. Governments and private sector investors are also supporting companies that make animal feed protein from microorganisms as it is one of the most sustainable sources of protein for animal nutrition. For instance, in February 2022, Arbiom—a French American manufacturer of high-quality proteins for animal feed and food applications by processing agricultural waste and wood residues—received an investment of US$ 13.50 million from the France Relance investment program. After receiving the investment, the company announced the construction of its first commercial production plant in France. Thus, the rising government and private sector investment in the microbial protein for feed market is expected to positively impact the market growth over the forecast period.
Source Insights
Based on source, the global microbial protein for feed market is segmented into bacteria, yeast, and others. The bacteria segment held the largest share of the global microbial protein for feed market in 2021 and is expected to register the highest CAGR from 2022 to 2028. Bacteria exhibit the highest growth rates compared to yeast and other microorganisms. Moreover, the amount of protein produced using bacterial culture is the largest. Furthermore, it has more than 70% crude protein and has a favorable essential amino acid profile. According to various studies, 1,000 kg bacteria produce a larger quality of proteins than soybeans and beef cattle. Thus, bacteria are one of the cost-effective and fastest sources of protein for animal feed. All these factors are driving the market for the segment.
The key players operating in the global microbial protein for feed market include Calysta, Inc.; Avecom; Arbiom; KnipBio; ICC; and Alltech. Market players are focusing on providing high-quality products to fulfill customer demand. They are also focusing on strategies such as investments in research and development activities, partnerships, and expansion.
Microbial Protein Used in Feed
Microbial Protein for Feed Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market size in 2022 | US$ 141.1 Million |
| Market Size by 2028 | US$ 308.06 Million |
| Global CAGR (2022 - 2028) | 13.9% |
| Historical Data | 2020-2021 |
| Forecast period | 2023-2028 |
| Segments Covered |
By Source
|
| Regions and Countries Covered |
North America
|
| Market leaders and key company profiles |
|
Microbial Protein for Feed Market Players Density: Understanding Its Impact on Business Dynamics
The Microbial Protein for Feed Market is growing rapidly, driven by increasing end-user demand due to factors such as evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and greater awareness of the product's benefits. As demand rises, businesses are expanding their offerings, innovating to meet consumer needs, and capitalizing on emerging trends, which further fuels market growth.
Key Development:
In June 2022, Calysta Inc. and Adisseo formed a joint venture (JV), "Calysseo," to start their first industrial-scale production facility in Chongqing, China, to produce 20,000 tonnes of FeedKind, a microbial protein for aquafeed, annually. With the successful production and distribution of FeedKind in China, the JV partners are planning to expand the production capacity to 80,000 tonnes annually in the coming years.
Report Spotlights
- Progressive industry trends in the microbial protein for feed market to help players develop effective long-term strategies
- Business growth strategies adopted by developed and developing countries
- Quantitative analysis of the microbial protein for feed market from 2020 to 2028
- Estimation of global demand for microbial protein for feed
- PEST analysis to illustrate the political, economic, social, and technological factors impacting the global microbial protein for feed market growth.
- Recent developments to understand the competitive market scenario
- Market trends and outlook, as well as factors driving and restraining the growth of the microbial protein for feed market
- Assistance in the decision-making process by highlighting market strategies that underpin commercial interest, leading to the market growth
- Self-tanning products market size at various nodes
- Detailed overview and segmentation of the market, as well as the microbial protein for feed industry dynamics
- Size of the microbial protein for feed market in various regions with promising growth opportunities
Frequently Asked Questions
- Historical Analysis (2 Years), Base Year, Forecast (7 Years) with CAGR
- PEST and SWOT Analysis
- Market Size Value / Volume - Global, Regional, Country
- Industry and Competitive Landscape
- Excel Dataset
Recent Reports
Testimonials
Reason to Buy
- Informed Decision-Making
- Understanding Market Dynamics
- Competitive Analysis
- Identifying Emerging Markets
- Customer Insights
- Market Forecasts
- Risk Mitigation
- Boosting Operational Efficiency
- Strategic Planning
- Investment Justification
- Tracking Industry Innovations
- Aligning with Regulatory Trends







 Get Free Sample For
Get Free Sample For