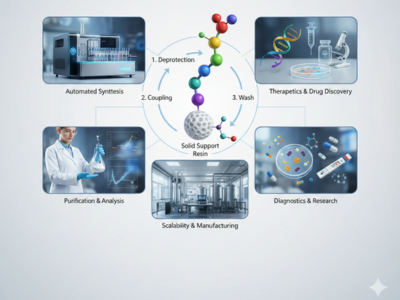
Peptide synthesis plays a critical role in modern pharmaceutical development, biotechnology research, and diagnostic innovation worldwide. Scientists rely on Peptide synthesis to construct short amino acid chains that replicate biological functions with high precision. Consequently, this capability supports drug discovery, therapeutic development, and advanced biomedical research. Among available methods, Solid Phase Peptide synthesis has emerged as the most reliable and efficient approach. Therefore, understanding its process, applications, and advantages remains essential for industry professionals.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Peptide Synthesis
Peptide synthesis refers to the chemical assembly of amino acids into a specific sequence using controlled reactions. Each amino acid links through peptide bonds, forming molecules with defined biological activity. Traditionally, solution-phase methods were used for Peptide synthesis; however, they introduced purification challenges and limited scalability. As a result, researchers transitioned toward solid-phase techniques to improve efficiency and reproducibility. Today, Solid Phase Peptide synthesis dominates both research and commercial manufacturing environments.
Overview of Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis
Solid Phase Peptide synthesis uses a solid support (usually an insoluble resin) to anchor the peptide chain being formed during the entire synthesis process. Chemists are able to add amino acids to the chain in a controlled manner, one at a time. The use of the solid support provides a simplified way to purify the peptide because it is easy to wash away excess reagents at the end of the reaction. As a result of these advantages, Solid Phase Peptide synthesis has made the synthesis of peptides much quicker, cleaner, and scalable. This new method has revolutionized the production of producing peptides on a global scale.
Step-by-Step Peptide Synthesis Process
Initially, peptide synthesis begins by attaching the first protected amino acid to a solid polymer resin to anchor the peptide for further growth of the chain. Once that initial bond has been made, chemists will remove the protecting group from the first amino acid via a deprotection reaction, thereby exposing a reactive site and enabling the next activated amino acid to couple with that site, thereby extending the peptide chain. After each coupling step, the chain is washed to remove any unreacted reagents and impurities prior to repeating this cycle until completion of the desired peptide sequence.
Once synthesis concludes, cleavage reagents will be used to cleave the peptide chain from the resin and remove any side-chain protecting groups. The peptide is then purified using chromatography or other purification methods to achieve the desired quality. The Peptide synthesis Process follows a specific methodology, thus providing reliable and consistent results while yielding a high-purity product.
Key Advantages of Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis
One significant advantage of Solid Phase Peptide synthesis is operational efficiency. Because the peptide remains bound to the resin, chemists can drive reactions to completion using excess reagents. Additionally, purification steps become simpler since washing replaces intermediate isolation. As a result, Peptide synthesis timelines shorten considerably.
Another major benefit involves automation compatibility. Automated synthesizers control reagent delivery, reaction time, and temperature precisely. Therefore, Peptide synthesis becomes highly reproducible and suitable for large-scale production. Automation also minimizes human error, which improves batch-to-batch consistency.
Flexibility and Customization in Peptide Synthesis
The pharmaceutical industry relies more on Peptide synthesis for the development of new drugs. Peptides show high specificity, biological activity, and lower toxicity than small molecules. Thus, they act as potent drugs for metabolic disorders, cancer, infectious diseases, and hormonal imbalances. Solid Phase Peptide synthesis facilitates the rapid development and large-scale production of peptide-based drugs. With the increasing demand, Peptide synthesis is leading the pharmaceutical industry.
Applications in Pharmaceutical Development
Pharmaceutical companies increasingly depend on Peptide synthesis to develop innovative therapies. Peptides demonstrate high specificity, strong biological activity, and reduced toxicity compared to small molecules. Therefore, they serve as effective treatments for metabolic disorders, cancer, infectious diseases, and hormonal imbalances. Solid Phase Peptide synthesis supports rapid development and scalable manufacturing of peptide-based drugs. As demand grows, Peptide synthesis continues to drive pharmaceutical innovation.
Role of Peptide Synthesis in Diagnostics and Research
In addition to therapeutic applications, Peptide synthesis is also important in the development of diagnostics and other biomedical applications. In diagnostics, there is a need for peptides with specific sequences and predictable properties. Solid-phase peptide synthesis provides peptides with consistent properties for use in diagnostics. In biomedical research, peptides are used as tools to investigate protein-protein interactions, receptor signaling, and other cellular processes.
Technological advancements also played a critical role in accelerating the growth of the peptide synthesis market. Improvements in solid-phase peptide synthesis(SPPS), automation, and purification technologies have significantly enhanced production efficiency, reduced synthesis time, and improved product quality. Automated peptide synthesizers and advanced chromatography systems allow manufacturers and research institutions to produce complex peptides with greater accuracy and reproducibility, making peptide synthesis more accessible and cost-effective.
Scalability and Commercial Manufacturing
Scalability represents another major strength of modern Peptide synthesis techniques. Solid Phase Peptide synthesis allows seamless transition from laboratory-scale research to commercial manufacturing. Manufacturers can produce peptides in kilogram quantities while maintaining purity and reproducibility. This scalability proves essential for contract development and manufacturing organizations supplying clinical and commercial peptide APIs. Therefore, Peptide synthesis supports both innovation and industrial production needs.
Limitations and Challenges in Peptide Synthesis
Despite its advantages, there are some challenges associated with Peptide synthesis. In the case of longer peptide sequences, there may be lower coupling efficiency because of steric hindrance. Moreover, the use of specialized reagents and equipment leads to higher production costs. Nevertheless, continuous research and development efforts in resins, coupling reagents, and automation technology are overcoming these drawbacks. As a result, Solid Phase Peptide synthesis remains the most popular technique for most peptide uses.
Future Trends in Peptide Synthesis
Technology innovation is constantly enhancing the abilities of Peptide synthesis. Microwave-assisted synthesis, solid supports, and green chemistry are some of the methods that enhance efficiency and sustainability. In addition, the latest automation technology allows for rapid production and precise control of complex sequences. This ensures that Peptide synthesis remains up to date with the growing demands of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
Conclusion
Peptide synthesis has become an indispensable technology in modern life sciences, with Solid Phase Peptide synthesis leading the field. By offering efficiency, flexibility, scalability, and precision, this method supports therapeutic development, diagnostics, and research innovation. As the demand for peptide-based solutions continues to rise, Peptide synthesis will remain central to pharmaceutical progress and scientific advancement.