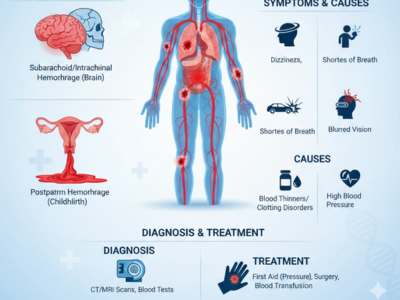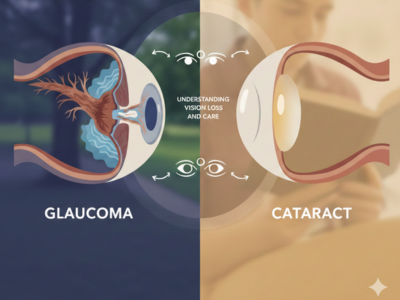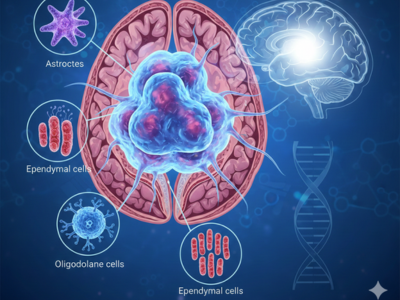
Radiation Therapy is a widely used cancer treatment that helps destroy cancer cells and control tumor growth effectively. It plays a crucial role either alone or combined with surgery and chemotherapy. Although Radiation Therapy targets cancer cells precisely, it can also affect nearby healthy tissues, which leads to side effects. Understanding what happens before, during, and after Radiation Therapy helps patients prepare confidently and manage their treatment journey smoothly.
What Is Radiation Therapy and How Does It Work
Radiation Therapy uses high-energy radiation beams to damage cancer cells' DNA and prevent further cell division. Because the treatment focuses on specific body areas, it limits unnecessary exposure to healthy tissues. However, some normal cells still get affected during Radiation Therapy, and this interaction causes temporary or long-term side effects. The severity of these effects depends on radiation dose, treatment duration, and the targeted body region.
What to Expect Before Radiation Therapy
Treatment Planning and Preparation
Before Radiation Therapy begins, a treatment plan is developed based on imaging scans to identify the location of the tumor. According to healthcare professionals, patient education on treatment schedules, side effects, and home care is also provided to those scheduled to undergo Radiation Therapy.
Emotional and Physical Readiness
Patients often experience anxiety before starting Radiation Therapy. However, understanding that the treatment itself is painless helps reduce fear. Asking questions and discussing expectations allows patients to feel emotionally prepared and physically confident before therapy begins.
Common Side Effects During Radiation Therapy
Fatigue and Energy Changes
Fatigue is among the most frequent reactions that occur while undergoing radiation therapy. Patients can experience undue fatigue even after resting adequately. Fatigue progressively accumulates throughout the course of this treatment. Therefore, balancing rest with light physical activity and maintaining proper nutrition helps manage energy levels effectively.
Skin Changes in the Treated Area
Radiation Therapy may impact the skin through which the radiation is administered. Patients may experience erythema, dryness, itching, or skin sensitivity, which may resemble a sunburn. Such reactions may appear a few sessions into radiation treatment.
Hair Loss in the Radiation Field
Radiation Therapy may cause hair loss only in the treated area. For example, scalp treatment may lead to localized hair thinning or hair loss. In most cases, hair begins to regrow after treatment completion, although texture or thickness may differ from before.
Radiation Therapy Side Effects by Treatment Area
Head and Neck Radiation Therapy
Radiation Therapy targeting the head and neck region can cause dry mouth, a sore throat, changes in taste, and difficulty swallowing. These effects occur because salivary glands and oral tissues are sensitive to radiation exposure. Maintaining oral hygiene and following dietary adjustments can significantly reduce discomfort.
Chest Radiation Therapy
When Radiation Therapy targets the chest, patients may experience coughing, throat irritation, or mild chest discomfort. These symptoms usually develop gradually. Reporting symptoms early allows for timely medical support and prevents complications.
Abdominal and Pelvic Radiation Therapy
Radiation Therapy to the abdomen or pelvis can affect digestion and bladder function. Patients may notice nausea, diarrhea, appetite changes, or frequent urination. Staying hydrated and following recommended dietary guidelines helps manage these side effects effectively.
Emotional and Psychological Effects of Radiation Therapy
In addition to physical symptoms, Radiation Therapy may impact emotional well-being. Patients can experience anxiety, stress, or mood changes during treatment. Emotional support, counseling, and connecting with supportive networks help patients maintain mental resilience and emotional balance throughout therapy.
Projected Cancer Prevalence
According to the WHO, new cancer cases are forecasted to be over 35 million in 2050, a 77% increase from the estimated 20 million cases in 2022. The rapidly growing global cancer burden reflects both population aging and growth, as well as changes to people's exposure to risk factors, several of which are associated with socioeconomic development. Tobacco, alcohol, and obesity are key factors behind the increase in cancer incidence, while air pollution remains a major driver of environmental risk factors.
It can be used any time during the course of treatment and often is combined with other treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and others.
What to Expect After Radiation Therapy
Recovery After Treatment Completion
After Radiation Therapy ends, most short-term side effects gradually improve over several weeks. Skin reactions heal, fatigue decreases, and energy levels slowly return. Patients should continue following care instructions to support recovery.
Long-Term and Late Side Effects
Some Radiation Therapy side effects may appear months or years later. These late effects can include skin thickening, tissue stiffness, or scarring in the treated area. Regular follow-up visits help monitor recovery and address any delayed changes early.
Managing Radiation Therapy Side Effects Effectively
Lifestyle and Self-Care Strategies
Managing Radiation Therapy side effects requires consistent self-care. Eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients supports tissue repair and overall strength. Staying hydrated improves healing and reduces discomfort. Gentle physical activity also helps maintain stamina and reduce fatigue.
Skin Care During Radiation Therapy
Skin care during and after Radiation Therapy is important. Patients are generally advised to clean the treated areas carefully, avoid raising the skin temperature excessively, and protect themselves from direct sun exposure. Recommended moisturizers will also maintain healthy, comfortable skin.
Importance of Communication with Doctors
Open communication plays a vital role in managing Radiation Therapy side effects. Patients should report new or worsening symptoms promptly. Early intervention improves comfort and enhances treatment outcomes.
Conclusion: Facing Radiation Therapy with Confidence
Radiation Therapy remains one of the most effective cancer treatment options available today. Although side effects are common, most are manageable with proper care, awareness, and timely support. By understanding what to expect before, during, and after Radiation Therapy, patients can approach treatment with confidence and clarity. Staying informed, proactive, and emotionally supported allows patients to focus on healing and recovery while maintaining quality of life throughout their cancer journey.