3D Sensors Market Overview and Growth by 2027
3D Sensors Market to 2027 - Global Analysis and Forecasts By Technology (Stereo Vision, Time-Of-Flight, and Structured Light); End-user Verticals (Healthcare, Aerospace, Industrial, Automotive, Consumer Electronics, and Others)
Historic Data: 2016-2017 | Base Year: 2018 | Forecast Period: 2019-2027- Report Date : Dec 2019
- Report Code : TIPTE100000302
- Category : Electronics and Semiconductor
- Status : Published
- Available Report Formats :


- No. of Pages : 150
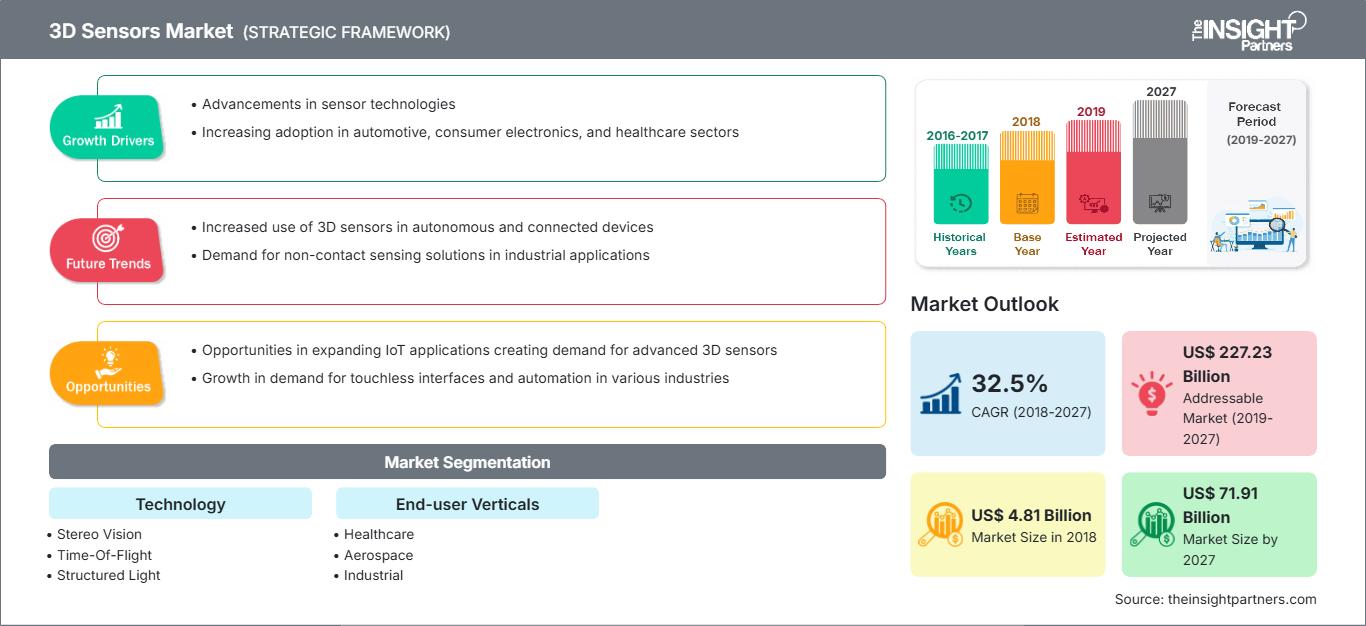
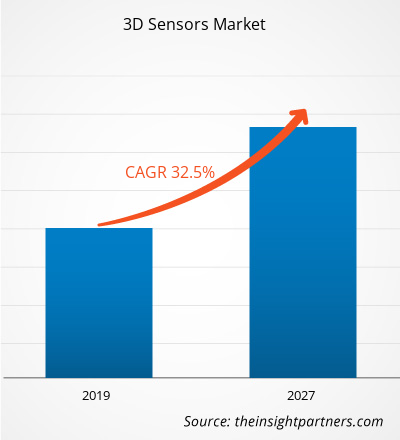
[Research Report] The 3D sensors market was valued at US$ 4,805.7 million in 2018 and is projected to reach US$ 71,914.2 million by 2027; it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 32.5% during 2019–2027.
3D sensors use active-range sensors that provide depth images at high frame rates. These cameras are equipped with an IR light source that illuminates the field, and a CMOS/CCD sensor that captures the reflected IR light. The depth measurement is based on the ToF principle; thus, the depth is proportional to the time spent by the IR signal to reach the object or filed of observation and come back. The depth measurements obtained for each pixel of the sensor together produce a depth image. The fast acquisition of depth images is of great use in a wide range of end-user verticals, such as robotics, human–machine interaction, and scene modeling. Unfortunately, many of the currently available ToF cameras have low resolutions and are affected by different measuring errors, including noise caused by sensors, systematic wiggling error due to the difficulty of generating sinusoidal signals, a non-linear depth offsets dependent on reflectivity and integration-time, and the flying pixels generated by the superposition of signals at depth inhomogeneities (edges). As a result, ToF sensors provide accurate and precise depth measurements. The currently available multi-ToF sensor systems focus on combining depth images to build 3D reconstructions by relying on occupancy probability grids or registering the point clouds generated from different views, etc.
The ToF techniques have been in use for more than a decade for ranging purposes. SONAR and RADAR are the two techniques that exploit sound and radio signals of ToF principles, particularly in aerospace and aeronautic end-user verticals. More recently, with the improvement and the maturity of electronic devices, it has been possible to employ light signals for ToF systems. End-user verticals using such a system are numerous, especially in industrial and consumer fields. In general, there are two techniques of measuring distance with modern ToF sensors: pulsed-modulation or continuous-wave (CW) modulation. Advanced ToF systems deploy multi-frequency technologies, combining more modulation frequencies.
Customizee This Report To Suit Your Requirement
Get FREE CUSTOMIZATION3D Sensors Market: Strategic Insights
-
Get Top Key Market Trends of this report.This FREE sample will include data analysis, ranging from market trends to estimates and forecasts.
Market Insights–3D Sensors Market
Increased Demand for Smart Consumer Electronics
The consumer electronics industry is witnessing immense growth in both developed and developing countries, and advancements and smart features that are offered by the manufacturing companies have been the major contributors to this growth.
Currently, various consumer electronics devices are used by individuals for a plethora of tasks. Consumer electronics such as smartphones, tablets, PCs, TVs, washing machines, fridge, and music players have become integral part of routine lives. All these devices are becoming smarter with the ongoing technological advancements and integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). The advancements in the sensor technology has paved the way for remarkable growth of IoT and AI in most of the technological arenas including the automotive sector. The market for consumer electronics devices is constantly growing with the manufacturers coming up with advanced technologies and features in their devices on a regular basis and rising disposable incomes of users in the developed and developing economies.
Some of the prominent smartphone manufacturers have pioneered the integration of 3D ToF sensors into their smartphone models. Leading global smartphone manufacturers such as Huawei, Samsung, Oppo, LG, and Apple are the pioneers in the integration of 3D ToF sensors into various models. Huawei P30 Pro, Samsung Galaxy S10 5G, Oppo RX17 Pro, Honor View 20, LG G8 ThinQ, and iPhone 2020 models have integrated or have planned to integrate the 3D ToF sensors into the models.
End-User Verticals Segment Insights
Based on end-user verticals, the 3D sensors market is segmented into healthcare, aerospace, industrial, automotive, consumer electronics, and others. Gadgets that were once bulky are now becoming more lightweight and miniaturized, with sensors that can gauge shapes in real time. A large number of new applications are coming up in the market due to speedy technological advancements. These technologies are now offering huge opportunities across different industry verticals, such as automotive, defense, healthcare, aerospace, robotics, electronics consumables, semiconductors, and retail, where 3D sensors can be used. Companies are now creating partnerships and increasing their collaborative efforts to bring more 3D applications.
Technology Segment Insights
Based on technology, the 3D sensors market is bifurcated into stereo vision, time-of-flight, and structured light. 3D sensors play a pivotal role in depth sensing to link devices in the real world. Continuous advancements in 3D sensors through comprehensive R&D have fueled creativity in the market for 3D sensors. Apart from being adopted in automotive, healthcare, robotics, and defense, 3D sensors are widely used in consumer electronics such as televisions, smartphones, and laptops. 3D sensors are also incorporated in wearable devices in addition to nanotechnology. Moreover, smartphone manufacturers are trying to incorporate 3D sensing technology in gaming and face recognition, among others. In the healthcare industry, 3D sensors assist in viewing the inner layers of skin, tumors, and veins. In the automotive industry, 3D sensors are widely used to get alerts in case of collision or imminent danger to avoid accidents. K-Series, iGPS, Laser line scanners, Laser Radar are among the products that are used in the aerospace and defense industry. The applications of 3D sensors will keep growing as there are novel inventions in electronics, automotive, and other industries.
The market players focus on new product innovations and developments by integrating advanced technologies and features in their products to compete with the competitors.
- 2019: AMS AG introduces a new ASV technology product portfolio that enables manufacturers of consumer, computing and industrial products to implement face recognition and other 3D sensing applications more easily and at a lower cost. Based on extensive 3D experience, ams has added Active Stereo Vision technology products to the portfolio to address additional and different 3D sensing applications as well as reach lower price points in the mobile segment. Also, AMS AG announced its partnership with SmartSens Technology, with this partnership AMS further expands its portfolio of three 3D technologies such as Time-of-Flight (ToF), active Stereo Vision (ASV), and Structured Light (SL) as well as accelerating time to market its new products.
The regional trends and factors influencing the 3D Sensors Market throughout the forecast period have been thoroughly explained by the analysts at The Insight Partners. This section also discusses 3D Sensors Market segments and geography across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East and Africa, and South and Central America.
3D Sensors Market Report Scope
| Report Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Market size in 2018 | US$ 4.81 Billion |
| Market Size by 2027 | US$ 71.91 Billion |
| Global CAGR (2018 - 2027) | 32.5% |
| Historical Data | 2016-2017 |
| Forecast period | 2019-2027 |
| Segments Covered |
By Technology
|
| Regions and Countries Covered |
North America
|
| Market leaders and key company profiles |
|
3D Sensors Market Players Density: Understanding Its Impact on Business Dynamics
The 3D Sensors Market is growing rapidly, driven by increasing end-user demand due to factors such as evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and greater awareness of the product's benefits. As demand rises, businesses are expanding their offerings, innovating to meet consumer needs, and capitalizing on emerging trends, which further fuels market growth.
- Get the 3D Sensors Market top key players overview
The Global 3D Sensors Market has been Segmented as Follows:
Global 3D Sensors Market – By Technology
- Stereo Vision
- Time-Of-Flight
- Structured Light
Global 3D Sensors Market – By End-user Verticals
- Healthcare
- Aerospace
- Industrial
- Automotive
- Consumer Electronics
- Others
Global 3D Sensors Market – By Geography
-
North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
-
Europe
- Germany
- France
- Italy
- United Kingdom
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
-
Asia Pacific (APAC)
- China
- Australia
- India
- Japan
- South Korea
- Rest of Asia Pacific
-
Middle East and Africa (MEA)
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- UAE
- Rest of Middle East and Africa
-
South America
- Argentina
- Brazil
- Rest of South America (SAM)
Company Profiles
- AMS AG
- Infineon Technologies AG
- Ifm Electronic Gmbh
- Melexis
- Sony Corporation
- STMicroelectronics N.V.
- Basler AG
- Cognex Corporation
- OmniVision Technologies, Inc.
- LMI Technologies Inc.
Frequently Asked Questions
Naveen is an experienced market research and consulting professional with over 9 years of expertise across custom, syndicated, and consulting projects. Currently serving as Associate Vice President, he has successfully managed stakeholders across the project value chain and has authored over 100 research reports and 30+ consulting assignments. His work spans across industrial and government projects, contributing significantly to client success and data-driven decision-making.
Naveen holds an Engineering degree in Electronics & Communication from VTU, Karnataka, and an MBA in Marketing & Operations from Manipal University. He has been an active IEEE member for 9 years, participating in conferences, technical symposiums, and volunteering at both section and regional levels. Prior to his current role, he worked as an Associate Strategic Consultant at IndustryARC and as an Industrial Server Consultant at Hewlett Packard (HP Global).
- Historical Analysis (2 Years), Base Year, Forecast (7 Years) with CAGR
- PEST and SWOT Analysis
- Market Size Value / Volume - Global, Regional, Country
- Industry and Competitive Landscape
- Excel Dataset
Recent Reports
Related Reports
Testimonials
The Insight Partners' SCADA System Market report is comprehensive, with valuable insights on current trends and future forecasts. The team was highly professional, responsive, and supportive throughout. We are very satisfied and highly recommend their services.
RAN KEDEM Partner, Reali Technologies LTDsI requested a report on a very specific software market and the team produced the report in a few days. The information was very relevant and well presented. I then requested some changes and additions to the report. The team was again very responsive and I got the final report in less than a week.
JEAN-HERVE JENN Chairman, Future AnalyticaWe worked with The Insight Partners for an important market study and forecast. They gave us clear insights into opportunities and risks, which helped shape our plans. Their research was easy to use and based on solid data. It helped us make smart, confident decisions. We highly recommend them.
PIYUSH NAGPAL Sr. Vice President, High Beam GlobalThe Insight Partners delivered insightful, well-structured market research with strong domain expertise. Their team was professional and responsive throughout. The user-friendly website made accessing industry reports seamless. We highly recommend them for reliable, high-quality research services
YUKIHIKO ADACHI CEO, Deep Blue, LLC.This is the first time I have purchased a market report from The Insight Partners.While I was unsure at first, I visited their web site and felt more comfortable to take the risk and purchase a market report.I am completely satisfied with the quality of the report and customer service. I had several questions and comments with the initial report, but after a couple of dialogs over email with their analyst I believe I have a report that I can use as input to our strategic planning process.Thank you so much for taking the extra time and making this a positive experience.I will definitely recommend your service to others and you will be my first call when we need further market data.
JOHN SUZUKI President and Chief Executive Officer, Board Director, BK TechnologiesI wish to appreciate your support and the professionalism you displayed in the course of attending to my request for information regarding to infectious disease IVD market in Nigeria. I appreciate your patience, your guidance, and the fact that you were willing to offer a discount, which eventually made it possible for us to close a deal. I look forward to engaging The Insight Partners in the future, all thanks to the impression you have created in me as a result of this first encounter.
DR CHIJIOKE ONYIA MANAGING DIRECTOR, PineCrest Healthcare Ltd.Reason to Buy
- Informed Decision-Making
- Understanding Market Dynamics
- Competitive Analysis
- Identifying Emerging Markets
- Customer Insights
- Market Forecasts
- Risk Mitigation
- Boosting Operational Efficiency
- Strategic Planning
- Investment Justification
- Tracking Industry Innovations
- Aligning with Regulatory Trends



















 Get Free Sample For
Get Free Sample For